New Data
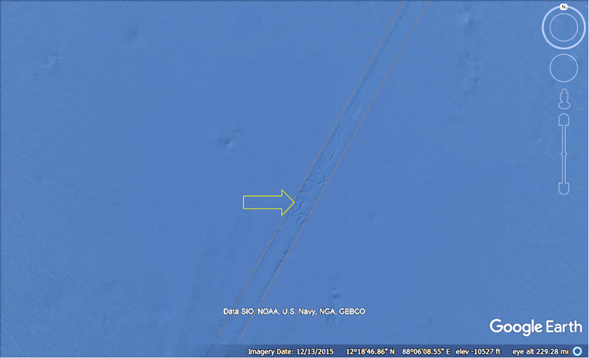
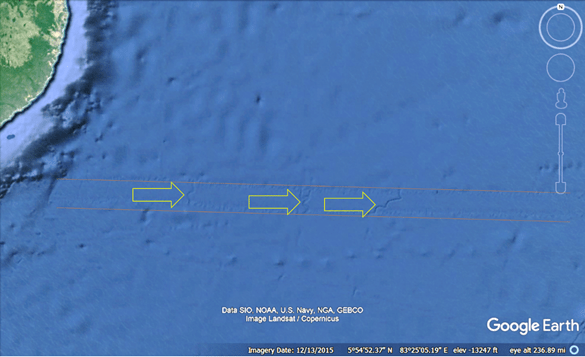
The images in Figure 1 (a)-(d) depict submerged landscapes from around the planet. Such maps represent new data, as they became ubiquitously available circa 2010. In each figure the white arrows identify submerged rivers and drainage systems that appear to be well-preserved. Many of the systems find their terminus hundreds of kilometers from present coasts and at depths greater than 3000 meters below present sea level.
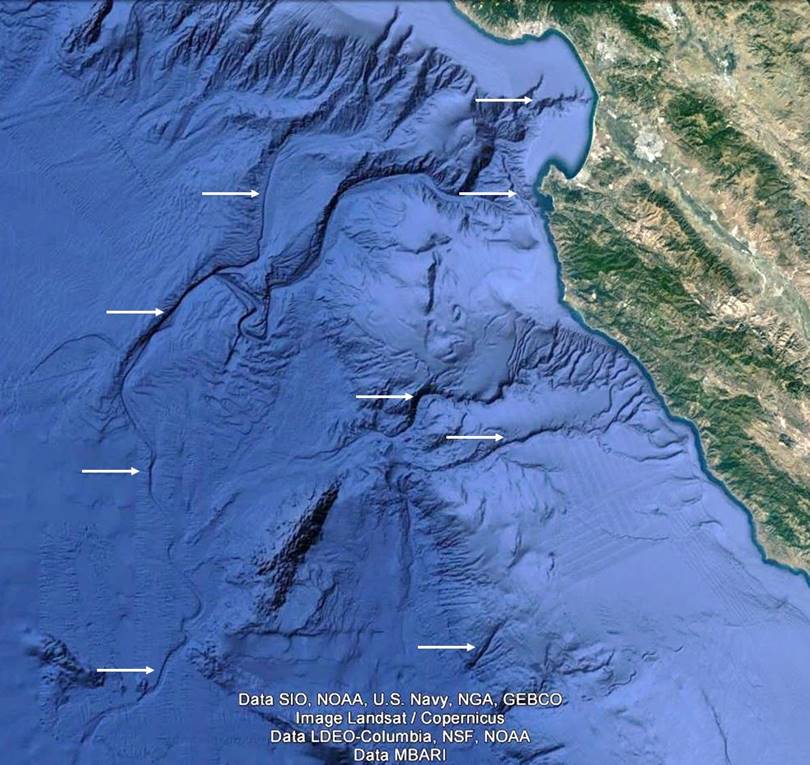
Figure 1(a). The bathymetry off Monterey, California.

Figure 1(b). The bathymetry off the Gulf of Alaska. Note in the lower right that the former river meandered between two volcanoes.
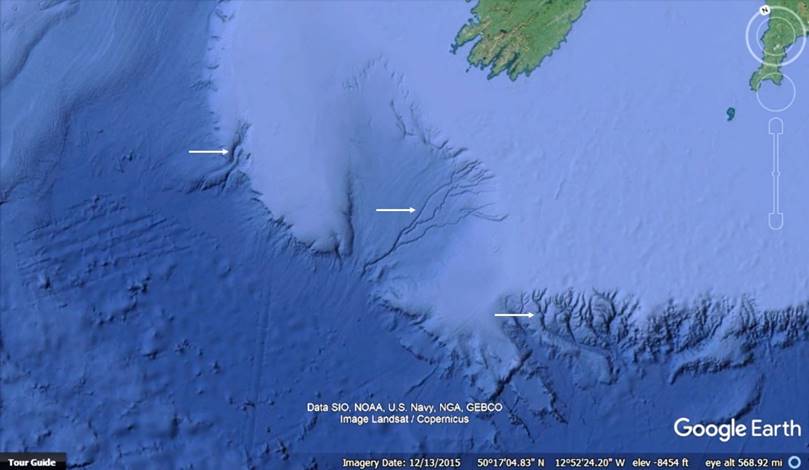
Figure 1(c). A bathymetry map of the Celtic Sea.

Figure 1(d). A bathymetry map of the Western Mediterranean Sea.
Geologists believe that these submerged structures were carved by subsurface processes because their science holds that there was never a worldwide flood. This exemplifies fitting data (submerged structures) to theory (No Flood), which is unscientific. This motivates a review of geology’s No Flood tenet.
No Flood
Geology’s prevailing No Flood paradigm finds its origin in the early decades of the nineteenth century when scientists in Europe debated whether the whole of the Earth suffered a deluge. Geologists set about various parts of the continent and discovered that diluvial deposits belonged to multiple, distinct events; some were found to have been transported by glaciers. Thus, at its essence, the argument against The Flood went like this: because there was no common event in the diluvial records, there could never have been a single worldwide flood.
Several key figures influenced the debate, among them the Reverend Adam Sedgwick, Woodwardian Professor at Cambridge University, and for two years president of the Geological Society of London. At the Society’s 1831 annual meeting, in his farewell address as president, Sedgwick recanted his belief in The Flood (italics added):
“The vast masses of diluvial gravel . . . do not belong to one violent and transitory period. It was indeed a most unwarranted conclusion when we assumed the contemporaneity of all the superficial gravel on the earth. . . . Having been myself a believer [in a worldwide flood], and, to the best of my power, a propagator of what I now regard as a philosophic heresy, . . . I think it right . . . thus publicly to read my recantation.”[1]
Sedgwick’s standing as the Society’s president, as a Cambridge University professor, and as a reverend played an important role in imparting lasting effect to his recantation: Geology’s “no worldwide flood, ever” paradigm persists to the present.
No Flood has far-reaching effect not only in geology but also in associated disciplines such as anthropology, archaeology, and human history. This was an historic, celebrated, and influential finding. An example of its status is found in Stephen Gould’s The Flamingo’s Smile, Reflections in Natural History, in which he praises Sedgwick’s scientific spirit: “I know no finer statement in all the annals of science than Sedgwick’s forthright recantation . . . it illustrated so well the difference between dogmatism, which cannot change, and true science.”[2] Sedgwick’s pronouncement rendered culturally independent, ubiquitous, ancient accounts of The Flood as either fantasies or exaggerations of local events. Thus, it is unsurprising that Pope Francis would claim, “The biblical flood, according to experts, is a mythical tale.”[3]
The No Flood Error
In drawing their “no worldwide flood, ever” conclusion, Sedgwick and his contemporaries did not consider that landscapes now submerged might once have been subaerial. Instead, they assumed that evidence of the flood would be found in presently exposed landscapes, which is not necessarily true, for The Flood could have filled the abyss from the depths upward. These early geologists assumed that the present amount of water has been with the earth since its beginning, thereby precluding the possibility that now-submerged landscapes were at one time exposed but later inundated.
The early geologists’ precise conclusion from the evidence before them should have been: a worldwide flood did not inundate presently exposed landscapes. This is completely and undeniably true, and no one can or would argue against the fact that presently subaerial landscapes were never submerged by a common flood event. That a worldwide flood did not inundate presently exposed landscapes is wholly different from geology’s claim that there was never a worldwide flood; the early geologists mistakenly passed judgment on the morphology of vast landscapes that they could not observe. Had the early geologists correctly concluded that a worldwide flood did not inundate presently subaerial landforms, they would have left open the Flood/No Flood matter until detailed bathymetry evidence could address the matter definitively, something accomplished by the submerged rivers and drainages in Figure 1.
The Flood and the Younger-Dryas Event are synonymous
The drainage systems identified in Figure 1 and the many others found throughout the planet were subaerially carved and seeking their terminal bodies of water. Thus, for the period required for flowing water to carve the myriad now-submerged drainage systems – and for the entire time preceding it, the Earth had substantially less water than the present. In addition, because the drainage systems are well preserved, they must have been covered in a relatively brief period. Furthermore, to cover the river systems by filling abyssal basins with more than 3 km of water requires an extra-terrestrial source since such a volume could not be stored in frozen form at the planet’s poles (insufficient room, as the atmosphere only extends so far). This implies that a cosmic impact delivered The Flood.
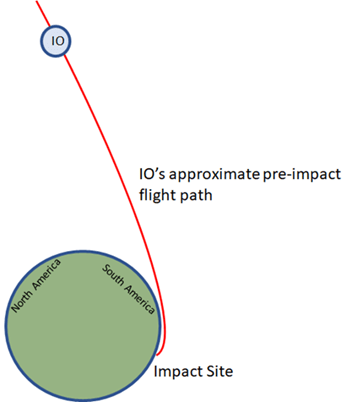
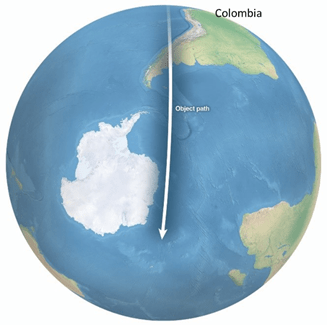
The Younger-Dryas (YD) event is an episode marked by abrupt increases in snowfall and dramatic changes to flora, fauna, mega fauna, climate, and the oceans[4], and it has been attributed by some to a cosmic impact roughly 12,800 years before present[5,6]. The impact is reported to have induced effects across at least four continents[7], and it also formed an associated layer of nanodiamonds[8], microscopic diamond crystals that are created by very high-velocity collisions, found across most of the planet[9]. Furthermore, the YD event caused sudden worldwide extinction of mammals weighing over 40 kg, as it is estimated that 82% of these animals disappeared in North America, 74% in South America, 71% in Australasia, 59% in Europe, 52% in Asia, and 16% in Sub-Saharan Africa. [10] Google Earth affords the identification of the YD impact site, as well as the determination of its size and approach direction. Furthermore, applying what is known of comet composition to the impact’s dimensions yields an approximation for the impact’s equivalent water volume, 1.29 * 109 km3, which corresponds to an average ocean depth of 3.57 km. The newly introduced waters flooded the planet, and they did so from the former abyss upward; the floodwaters did not inundate presently exposed landscapes. The worldwide flood instantiated ocean-driven global weather patterns as well as irreversible ecosystem and climatic changes. Back-propagating the trough carved by the celestial object’s solid nucleus indicates that it overflew Antarctica, South America, and North America on its impact approach. Ice and debris ejected along this path account for known YD impact sites in North America and South America. [11] Flood narratives from around the planet place the impact within the span of our collective oral and written traditions (notwithstanding the past two centuries). Thus, The Flood and the YD event are interchangeable terms.
The object that delivered The Flood
We will refer to the celestial object that delivered The Flood as Phaeton, though it is also known by other names such as Typhon, Set, Ta-vi, and Satan. It is interesting to consider its appearance as it neared Earth impact, particularly in the context that we can see small comets from millions of miles away. In contrast to Halley’s comet, Phaeton was on the order of 10,000 times larger by surface area and 1,000,000 times larger by volume. Therefore, Phaeton’s illumination and its prominent tail must have been frightening and memorable, particularly since The Flood ensued nearly immediately after its impact and disappearance. Pliny the Elder described Phaeton’s approach: “A terrible comet was seen by the people of Ethiopia and Egypt…. It had a fiery appearance and was twisted like a coil, and it was very grim to behold; it was not really a star so much as what might be called a ball of fire.”[12] According to Allan and Delair, Phaeton “was anciently regarded as a generally round, brilliantly fiery body of appreciable size, and much more star-like or sun-like than conventional comets: and it was held to have in some way caused the Deluge.”[13] Phaeton’s fiery, comet-like appearance as it neared Earth impact and the irreversible changes induced by its Flood likely account for the long-held notion that comets are harbingers of change. The Chinese New Year dragon, a glowing, fiery serpent depicted above the clouds with water emanating from its mouth, memorializes Phaeton’s frightening appearance and effects; it is plausible that the Chinese New Year is an annual commemoration of Phaeton’s impact. Due to its size, Phaeton was observable in the night sky for many years prior to impact, likely in the constellation known as Aquarius, the water bearer. Snake images carved into stone at the prehistoric observatory known at Göbekli Tepe almost certainly refer to Phaeton.
Our shared past: pre-Flood Earth
Figure 2 shows an ArcGIS-produced model of pre-Flood Earth with an estimated average of 3 km less water than the present. The figure shows that formerly exposed landscapes (tan and beige) were more abundant than those submerged (blue); vast seas and oceans existed, but they were disjointed – there was no common, pre-Flood sea level. Prior to The Flood, presently exposed landscapes (beige) were more than 3 km above abyssal landscapes. Earth’s atmosphere filled former abyssal regions, meaning that landscapes we now occupy (beige) would have been on the order of 50oF (or more) cooler than abyssal regions due to lesser atmospheric pressure. Earth’s tallest peaks were either at the top of the pre-Flood atmosphere or beyond it. The Flood’s waters are an immense heat sink; in their absence, abyssal Earth temperatures would have been much warmer, and polar ice regions would have been markedly smaller than the present.
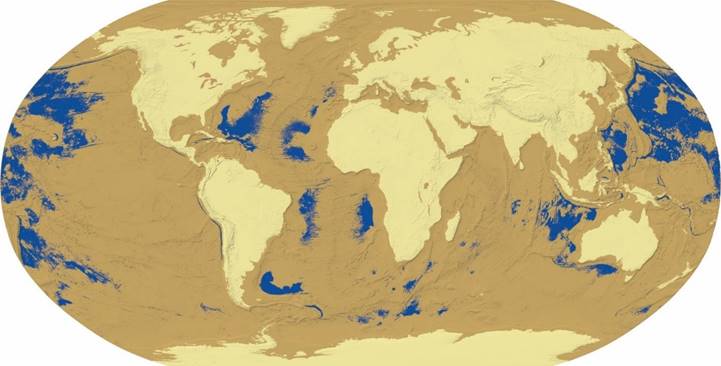
Figure 2. A model of land and sea distributions in pre-Flood Earth shows formerly subaerial but now-submerged landscapes (tan), presently exposed landscapes (beige), and former oceans and seas (blue). The pre-flood extent of the Mediterranean Sea is not shown as blue because the bottom of the basin is at an altitude above that used to create the tan regions.
Some implications and corrections
Abyss-dwelling species unable to flee upward to survivable landscapes would die. In addition, those species indigenous to presently exposed landscapes that were unable to cope with Flood-induced climatic changes would also perish (e.g. wooly mammoths). Humans are among the species whose homelands are now submerged beneath more than 3km of water. We survived upward, but planet-wide climatic changes render us ill-adapted to the Earth’s Post-Diluvian ecosystem. Other surviving, former abyss-dwellers were fortunate to find suitable habitats.
Although we will never know exactly what it was like in the abyssal, pre-Flood regions that we inhabited, our physical attributes lend insight. Certainly, it was much warmer, which accounts for our furless appearance. (Ecosystems that were more than 3 km above the abyss were much cooler, which is why our simian relatives have fur.) Human forays to pre-Flood upland regions would have required adaptive clothing. We need fresh water, so it is nearly certain that diverse cultures or clans shared abyssal fresh water sources. It is unlikely that there were pre-Flood cities because there was no need for the aggregation and distribution of resources: we were properly adapted, and suitable food was indigenous to our various habitats. (Atlantis was not a city; rather, it was a region through which an abundant fresh water source flowed, and its canals increased fresh water access for the clan.) The structure of our feet might indicate that we traversed sandy or soft domains. We walk upright, allowing us to see greater distances, indicating that our natural ecosystems might have been lightly forested.
The atmosphere was thicker above our abyssal homelands, and this caused the attenuation of UV and higher frequency sunlight, especially in locations further from the tropics. Diversity in human skin pigments and hair colors is a consequence of homelands’ latitudes north or south of the equator. Higher frequency light attenuation by a thicker atmosphere would also explain why humans only recently began to see blue.[14] Lesser atmospheric attenuation of starlight relative to that at abyssal depths would explain why the celestial observatory at Göbekli Tepe would be situated so far above the abyss.
Immediately after The Flood, human survival required stamina and problem-solving skills. Acquiring suitable foods, combatting cold environs, building shelters, and accomplishing simple tasks such as walking would favor those inclined to discovery and innovation. Ecosystem changes induced by the new oceans would cause migrations in search of suitable domains. The myriad survival tasks would be difficult, if not impossible, for an individual. Thus, our continued existence necessitates eusocial behaviors. Specialization in post-Flood survival-related skills would provide advantage to the clan; region-specific eusocial adaptations would lead to distinct cultures with associated, survival-related norms. Successful cultural norms, strategies, and implementations would foster larger populations which, in turn, would lead to greater demands for – and exploitation of – natural resources. Inevitably, migration and expansion would lead to clashes between clans.
Some claim that we are in a new geologic era, the Anthropocene, wherein human activity is the dominant influence on the environment. In the proper context that The Flood rendered us an ill-adapted species, the Anthropocene is the most recent ~12,800-year, post-Flood period during which humanity’s innate desire to survive, along with the associated demands that our ill-adaptation inflict on the environment, has dominated the planet.
Some recent findings in proper context
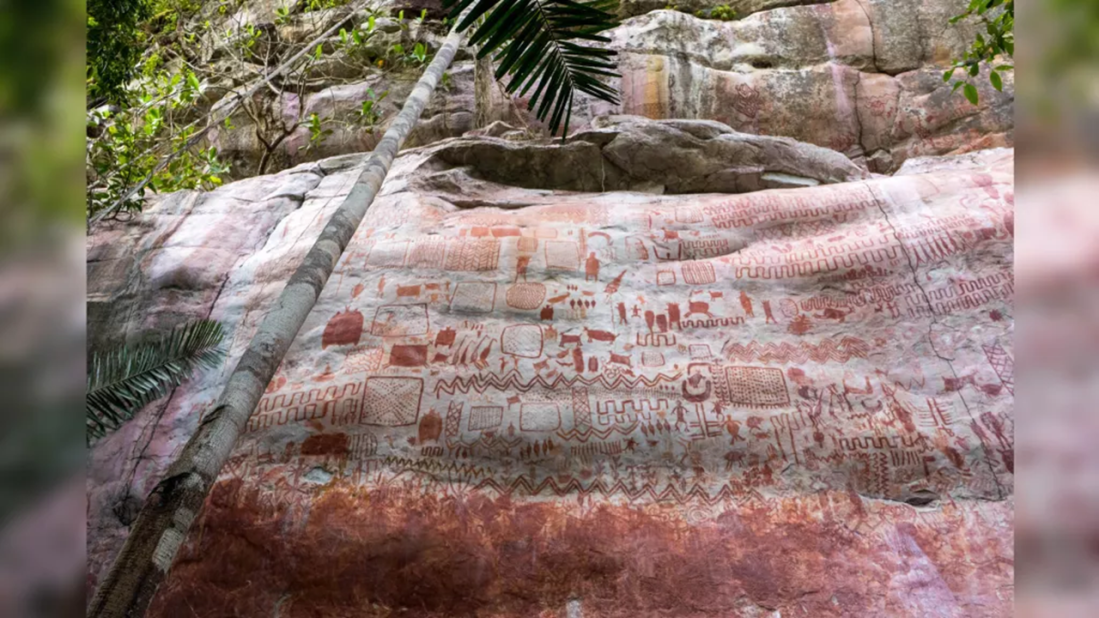
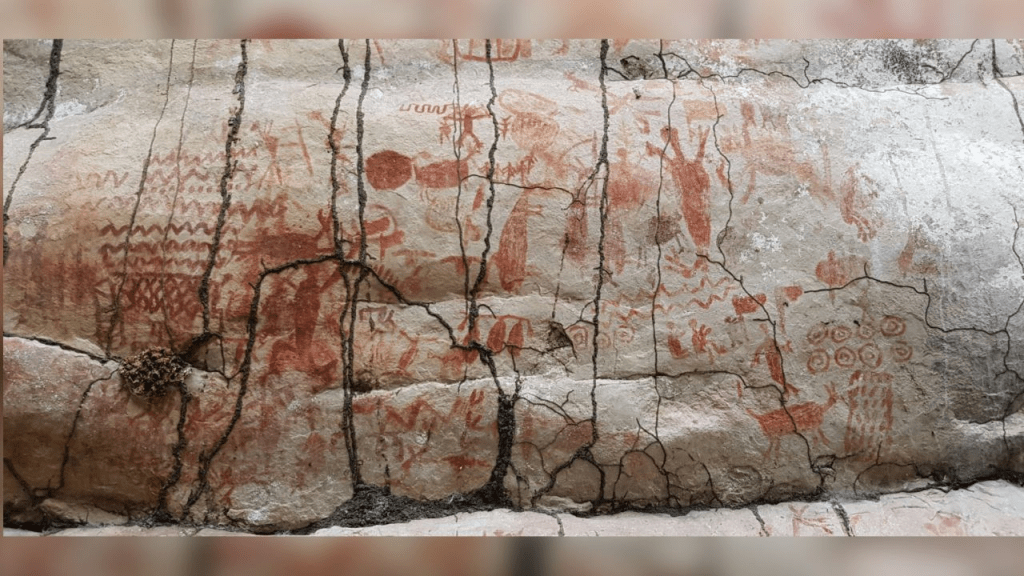
An eight-mile-long mural was recently discovered at Serranía La Lindosa on the northern edge of the Amazon in South America. Indigenous people started painting the images about 12,600 years before present, two-hundred years after The Flood. The mural includes handprints, geometric designs, and a wide array of humans, animals, hunting scenes, and images of people interacting with plants, trees, and savannah creatures. At the time the paintings were created, Flood-created ecosystem changes had the Amazon transforming from savannas, thorny scrub, and forests into today’s tropical rainforest.[15] The extensive mural commemorates this clan’s Flood survival endeavors and the many challenges brought by ill-adaptation. We should expect to find references to Phaeton somewhere on the mural since its approach path was directly above this region.
Geology’s error has created a gross misunderstanding of the peopling of the Americas, as we are led to believe that humans from Australia and other eastern Pacific regions made their way northward during an ice age, then eastward across a presumed land bridge into Alaska, and then down into South America. Human DNA similarities between indigenous people in Australia and the Amazon in South America put an end to that theory due to the absence of DNA similarities in regions through which the sojourners traveled (regions north of the Tropic of Cancer).[16] Instead, the DNA similarities are better understood in the context of pre-Flood Earth: a large clan spanned the pre-Flood abyssal Pacific basin. Today, descendants of Flood survivors from the west in Australia and in regional Pacific islands remain DNA-linked to descendants of flood survivors to the east in South America.
Like the many rivers and drainages in Fig. 1, the Flood waters preserved in the bathymetry many other geologic features and evidence. For instance, the discovery of a massive subglacial trough 300 km long, up to 25 km across, deeper than the Grand Canyon, and more than 2 km below present sea level [17], is easily understood in the context of pre-Flood Earth: the glaciers formed in Antarctica and flowed down into the former abyss, subaerially scouring the valley over the eons before the Flood.
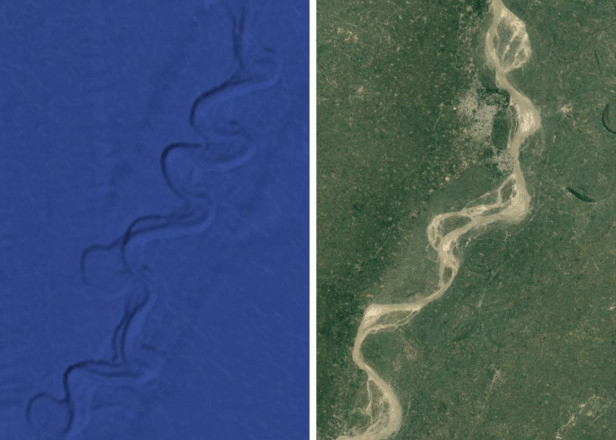
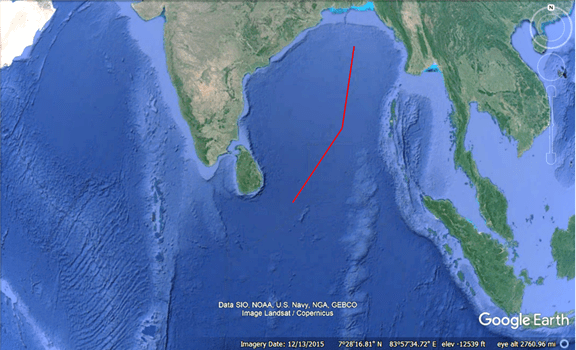
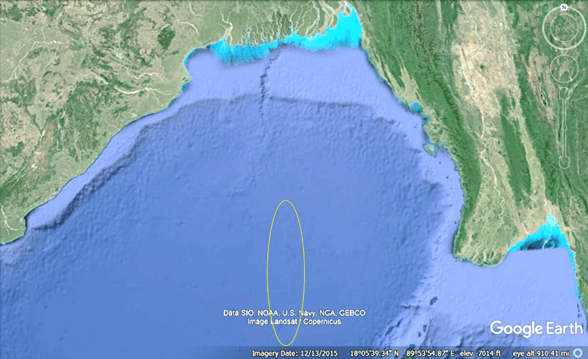
Similarly, International Ocean Discovery Program (IODP) Expedition 354 recently discovered abundant woody debris in the Bay of Bengal 3.7 km beneath the surface and preserved within coarse sediment layers of turbidite beds with recovery spanning 19 My, delivered episodically in high-magnitude, low-frequency wood export events.[18] The wood samples were found at various layers of core samples obtained 1600 km from where the Ganges and other systems flow into the Bengal Fan. Implied by the report is that somehow the tree fragments survived extensive transport and deposit in coarse sediments to become submerged beneath 3.7 km of water, millions of years apart, and at the exact location. Under No Flood, the transport and deposition mechanisms cannot be explained. However, in the proper context that there was a worldwide flood, the discovery of the wood samples from sandy cores is simply explained: prior to The Flood, the Ganges and other river systems carried water down the continental shelf and then southward into abyssal regions, and the rivers suffered episodic, high-magnitude, low frequency wood export events, or floods. Such floods were of sufficient velocity to transport coarse sediments that preserved the wood fragments in riparian regions. The age discrepancy in the recovered samples indicates that the river suffered floods for millions of years, and we now discover them submerged in the Bay of Bengal beneath 3.7 km of Flood water. For visual corroboration, the image on the left of Figure 3 identifies the drill location from which the IODP wood samples were obtained, and on the right is a portion of the present-day Ganges.
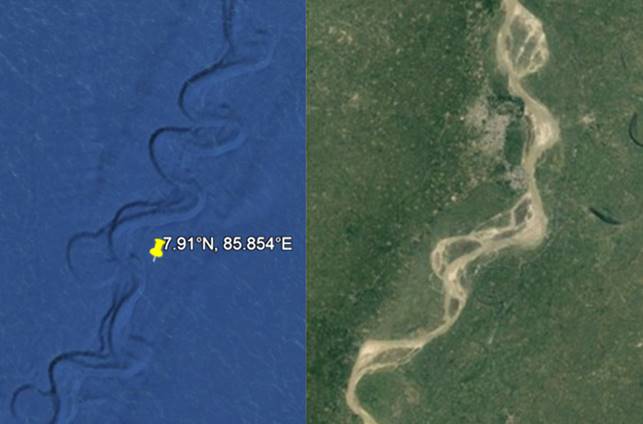
Figure 3. IODP Expedition 354 drill site’s location is indicated by the pin on the left image. On the right is a portion of the present-day subaerial Ganges.
Conclusions
Geology’s No Flood error is an historic blunder that adversely affects our understanding of what we are, where we are from, and what has happened to our planet. There was a worldwide flood ~12,800 years before present; The Flood and the Younger-Dryas event are equivalent terms. Humans are from abyssal regions now submerged in more than 3km water. Although we survived the event, we are ill-adapted to the post-Flood Earth ecosystem; our continued survival requires innovation and abuse of Earth’s natural resources. For two-hundred years, geology, archaeology, anthropology, and human pre-history have suffered from the No Flood error. These disciplines warrant complete review and correction based on the proper context that there was a worldwide flood.
References
[1] Sedgwick, A. 1831. Address to the Geological Society of London, on retiring from the President’s Chair, February 18.
[2] Gould, S.J. 1985. The Flamingo’s Smile: Reflections in Natural History. New York: W.W. Norton & Company.
[3] Pope Francis. 2021. Dei Vizi e delle Virtù. Rizzoli.
[4] Firestone R.B., West, A., Kennett, J.P., Becker, L., Bunch, T.E., Revay, Z.S., Schultz, P.H., Belgya, T., Kennett, D.J., Erlandson, J.M., Dickenson, O.J., Goodyear, A.C., Harris, R.S., Howard, G.A., Kloosterman, J.B., Lechler, P., Mayewski, P. A., Montgomery, J., Poreda, R., Darrah, T., Que Hee, S.S., Smith, A.R., Stich, A., Topping, W., Wittke, J.H. and Wolbach, W.S. (2007) Evidence for an extraterrestrial impact 12,900 years ago that contributed to the megafaunal extinctions and the Younger-Dryas cooling. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Vol. 104, iss. 41, 16016-16021.
[5] Holliday, V., Surovell, T., Meltzer, D., Grayson, D., Boslough, M. (2014) The Younger-Dryas impact hypothesis: a cosmic catastrophe. Journal of Quarternary Science, Vol. 29, issue 6, 515-530
[6] Wolbach, W. S., Ballard, J. P., Mayewski, P. A., Parnell, A. C., Cahill, N., Adedeji, V., Bunch, T. E., Dominguez-Vazquez, G., Erlandson, J. M., Firestone, R. B., French, T. A., Howard, G., Israde-Alcantara, I., Johnson, J. R., Kimbel, D., Kinzie, C. R., Kurbatov, A., Kletetschka, G., LeCompte, M. A., Mahaney, W. C., Melott, A., Mitra, S., Maiorana-Boutilier, A., Moore, C. R., Napier, W. M., Parlier, J., Tankersley, K. B., Thomas, B. C., Wittke, J.H., West, A., Kennett, J. P. (2018) Extraordinary Biomass-Burning Episode and Impact Winter Triggered by the Younger Dryas Cosmic Impact ∼12,800 Years Ago. 1. Ice Cores and Glaciers,” The Journal of Geology Vol. 126, iss. 2, 165-184. 2. Lake, Marine, and Terrestrial Sediments. The Journal of Geology Vol. 126, iss. 2, 185-205.
[7] Kennett J.P., D.J. Kennett, B.J. Culleton, J.E.A. Tortosa, J.L. Bischoff, T.E. Bunch, I.R. Daniel Jr., J.M. Erlandson, D. Ferraro, R.B. Firestone, A.C. Goodyear, I. Israde-Alcántara, J.R. Johnson, J.F. Jordá Pardo, D.R. Kimbel, M.A. LeCompte, N.H. Lopinot, W.C. Mahaney, A.M.T. Moore, C.R. Moore, J.H. Ray, T.W. Stafford Jr., K.B. Tankersley, J.H. Wittke, W.S. Wolbach, and A. West. 2015. Bayesian chronological analyses consistent with synchronous age of 12,835–12,735 Cal B.P. for Younger Dryas boundary on four continents. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 112 (32): E4344–E4353.
[8] Kennett, D. J., Kennett, J. P., West, A., Mercer, C., Que Hee, S. S., Bement, L., Bunch, T. E., Sellers, M., and Wolbach, W. S. (2009) Nanodiamonds in the Younger Dryas boundary sediment layer. Science, Vol. 323, iss. 5910, 94.
[9] Kinzie C.R., S.S. Que Hee, A. Stich, K.A. Tague, C. Mercer, J.J. Razink, D.J. Kennett, P.S. DeCarli, T.E. Bunch, J.H. Wittke, I. Israde-Alcántara, J.L. Bischoff, A.C. Goodyear, K.B. Tankersley, D.R. Kimbel, B.J. Culleton, J.M. Erlandson, T.W. Stafford, J.B. Kloosterman, A.M.T. Moore, R.B. Firestone, J.E. Aura Tortosa, J.F. Jordá Pardo, A. West, J.P. Kennett, and W.S. Wolbach. 2014. Nanodiamond-rich layer across three continents consistent with major cosmic impact at 12,800 Cal BP. The Journal of Geology 122 (5): 475–506.
[10] Firestone RB (2019) Disappearance of Ice Age Megafauna and the Younger Dryas Impact Capeia: 20190724.006
[11] Jaye, M (2019). The Flooding of the Mediterranean Basin at the Younger-Dryas Boundary. Mediterranean Archaeology and Archaeometry 19(1): 71-83.
[12] Rackham, H. (transl). 1938. Pliny the Elder Natural History (London); vol ii, p 91.
[13] Allan, D.S. and J.B. Delair. 1997. Cataclysm! Compelling Evidence of a Cosmic Catastrophe in 9500 B.C. Rochester, Vermont: Bear and Company. Originally published as When the Earth Nearly Died (Bath, England: Gateway Books, 1995).
[14] MacDonald, F (2018). There is evidence humans did not see blue until modern times. Science Alert, April 2018.
[15] Gaspar Morcote-Ríos, et. al. 2021. Colonisation and early peopling of the Colombian Amazon during the Late Pleistocene and the Early Holocene: New evidence from La Serranía La Lindosa. Quaternary International, 578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2020.04.026.
[16] Llamas, B., et. al. 2016. Ancient mitochondrial DNA provides high-resolution time scale of the peopling of the Americas. Science Advances 2 (4).
[17] Ross N., T. Jordan, R. Bingham, H. Corr, F. Ferraccioli, A. Le Brocq, D. Rippin, A. Wright, M. Siegert. 2013. The Ellsworth Subglacial Highlands: Inception and retreat of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet. Bulletin of the Geological Society of America, 19 Sept 2013.
[18] Hyejung Lee, Valier Galy , Xiaojuan Feng, and Sarah J. Feakins. 2019. Sustained wood burial in the Bengal Fan over the last 19 My. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 116 (45) 22518-22525 doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1913714116.